POSTS

MOTHERBOARD
A motherboard is a flat board with single, double up to 15 layers of conducting printed words and holes and solder pads to which chips or sockets carrying chips are connected. Beside the CPU socket (the rectangular black), it has many memory slots (the four back) and expansions slots (the white and many black ones), to have daughter boards. Size is normally one foot square but might be less or more based on the application. Small systems may have euro card size of 10cmx16cm, and servers may have larger one to hold more CPUs and memory modules. Today, many vendors produce Single Board Computer (SBC), a small 8cmx12 cm with various ports, and all you need is a keyboard, mouse and monitors to get a working system

SBC
The Single Board Computer (SBC) is a small PCB with few USB ports to connect to peripherals like keyboard, mouse, printer, etc. Ethernet part for networking, HDMI port to connect to a monitor, may also have micro SD card, may have a stand alone power jack unless it takes power from one of the ports (USB or Ethernet). The black metal frame is a heat sink. In addition to those ports, dual in line pins for input/output and others are available

MICROCONTROLLER
A small board with a microcontroller chip (black square in the middle) and few other chips and many general purpose input/output pins (black on the edges). Also has power supply port and a communication port to connect to a host for programming and data exchange. Normally enough memory of non-volatile read only and read/write are integrated within the microcontroller chip

EMBEDDED SYSTEM
A small computer subsystem within a system, it performs more functions that a controller, it may provide input/output, communication and even processing

SoC
System on Chip (SoC) packs a whole system on a chip for specific task. Shown is an ARM based, Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ Board, used to develop AI/ML Applications, IoT/Cloud connectivity, Embedded Computing and Robotics. It integrates 2 GB LDDR4 DRAM, USB ports, microSD card for booting, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and two low speed and high speed expansion headers in a small form factor. The power of this system comes from the FPGA that can tailored to support a wide range of applications
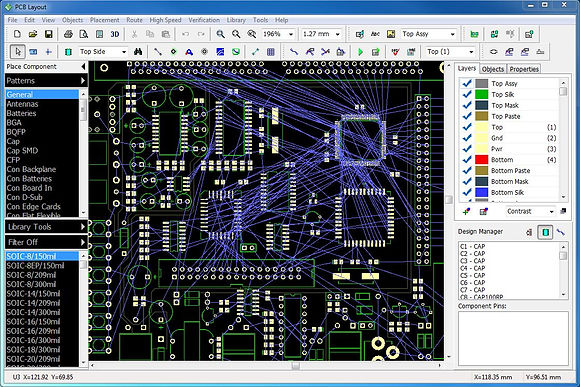
LAYOUT SOFTWARE
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout and routing software help designers place chips and other components and provide routing and vias from a net list entered by the designer. You can easily change the locations and see immediate change in routing. Advanced routing software support multi layer boards, and produce data files for automatic drilling, etching and silk screening machines
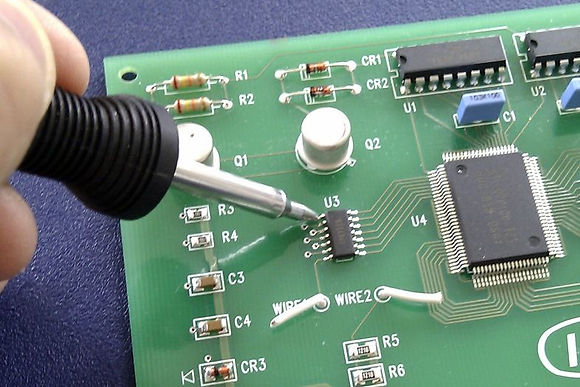
PCB
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a sheet of non-conductive material (fiber glass) as substrate and one, two or many copper sheets to provide connections between electronic parts. the sockets or parts are soldered using various techniques, and silk screened to have names of components for assembly and repair. An alternative to this is the wire wrapping, which is good only for prototyping

RTC
Real Time Clock (RTC) is a module or small PCB with a chip that integrates counting elements and several bytes of memory to store the seconds, minute, hour, day, week, month and year, and this read/write memory is backed by a small battery that can retain data and keep the counting elements ticking for a decade. Typically, when power is on it takes power form the system. Modern systems integrate this function within the chipset. The data exchange with the host is carried out via a serial protocol like I2C or SPI

PROTOTYPING
To prototype a small circuit, we can use the bread board or the wire wrapping board. The bread board is easy but good only for simple prototypes, while the wire wrapping boards required skills in wrapping and unwrapping wires to the pins of the socket, chip or headers. A bread board can easily get crowded as the wires and components are on the same side, while they are on opposite sides in the wire wrapping boards

SERVER
A powerful computing system with modular design for scalability; typically one or more racks with many blades; processors, communication fabric and storage media to support too many users and run too many applications. More of those is added as the enterprise grows