POSTS

HYPER SCALE DATA CENTERS
Most hyper-scale data centers belong to Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Facebook, and smaller ones like Twitter, eBay, Alibaba, and Baidu. There are more than 500 such data centers today. With $200 per square foot estimated cost to build a data center on an existing property, today's data centers easily exceed the billion dollar boundary. Lately, a hyper-scale data centers are being built at a rate of one every week

MCBFET 3nm
Multi Channel Bridge (MCB) FET is an enhancement to the Gate All Around technology (GAA). Samsung is about to release 3nm chip, to be launched in the market by 2021, as a breakthrough in the processor technology. The shrinking chip is all set to boost the speed of using by 35% and also will reduce power cutting by 50% and increase the area by 45%

NEURON CHIP
A tiny silicon microchips, nearly identical to biological nerve cells present in the human body, considered a paradigm changing as it provides a robust method to reproduce the electrical properties of real neurons in minute detail. Found able to recapitulate responses seen in real cells in 60 different stimulation protocols

AURORA
Intel’s data-centric silicon portfolio and oneAPI initiative lays the foundation for the convergence of HPC and AI workloads at exascale, building upon the Intel Xeon Scalable platform and using Xe architecture-based GPUs, as well as Intel Optane DC persistent memory and connectivity technologies. The compute node architecture of Aurora will feature two 10nm-based Intel Xeon Scalable processors (code-named “Sapphire Rapids”) and six Ponte Vecchio GPUs. Aurora will support over 10 PB of memory and over 230 PB of storage. Aurora will leverage the Cray Slingshot fabric to connect nodes across more than 200 racks

BINNING
Binning is a term vendors use for categorizing components, including CPUs, GPUs, RAM modules, by quality and performance. While components are designed to achieve a certain performance level, sometimes the final product fails to meet those standards, due to the complexities associated with manufacturing components. After manufacturing, vendors conduct testing and bin the component based on its performance results. For example, a quad core processor with max frequency of 4 GHz, with two cores failing to meet the speed and power test may be marked as dual core processor, or its max frequency set to 3 GHz. A 32 GB flash memory chips with many faulty blocks may get marked as 16 GB after disabling those blocks

EDGE COMPUTING
Edge computing is the practice of processing data near the edge of your network, where the data is being generated, instead of in a centralized data-processing warehouse. This reduces latency and bandwidth requirement and even the computing power needed in the cloud

DIFFERENCE ENGINE
Charles Babbage began to construct a small difference engine, mechanical computer, in 1819 and had completed it by 1822. The machine used the decimal number system and was powered by cranking a handle. In 1823, the British government gave Babbage £1700 to start work on the project, but the metalworking techniques of the era could not economically make parts in the precision and quantity required. In 1832, Babbage and Joseph Clement produced a small working model (one-seventh of the calculating section of Difference Engine, and was intended to operate on 20-digit numbers
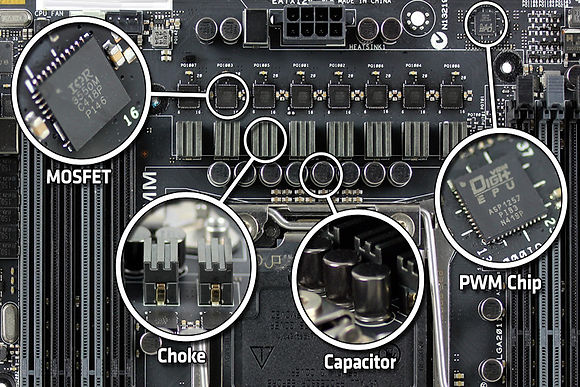
VRM / PPM
A Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) or Processor Power Module (PPM) is one of the components of the motherboard, its job is to supply a stable voltage to the CPU or GPU. It is a Buck step down DC-to-DC converter with efficiency that reaches 90% and has many phases, 4, 6, 8 or even 10 for smooth voltage and uses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal to reduce power consumption and overheating (typically 80 to 100 Celsius). Each phase consists of a set of MOSFET drivers, Chokes and Capacitors, to supply smooth and stable 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, ... or 2.0V regardless of current variations out of 12V DC from therein computer power supply. Modern CPUs have onboard regulator to supply 0.7 to 1.4 V to the cores as needed. Today's motherboards have such function integrated within the chip sets

SiP / MCM
System in Package (SiP), also referred to as a Multi-Chip Module (MCM), is an electronic device that looks like a single Integrated Circuit (IC). However, instead of just doing a single function, a SiP incorporates many different ICs into a single package. This one package can contain an entire electronic subsystem or even a complete system. Parts of SiP are less tight coupled compared to SoC. The SiP approach offers faster design cycle, simpler bill of material and hence smaller space, and possibly cheap and low power consumption solutions. Such a device may be the heart of a desktop computer soon, replacing a whole motherboard

LIQUID COOLING - OVERCLOCKING
Modern µP systems have chipsets that coordinate the work of the components. Typically the chipset generates a base clock, let us say 100 MHz, and supplies to the other components. The CPU, GPU and SDRAM use multipliers to get much higher rates, for example a CPU with x36 internal multiplier runs at 3.6 GHz, and can increase or decrease based on heating and need. It is necessary to do this for synchronization. The CPU can be overclocked to get few more hundreds of MHz, like if we adjust the multiplier to x38 we can run the processor at 3.8 GHz. This might offer small performance gain in compute-intensive applications but has risk of failure due to excessive heating, unless paper cooling, mostly liquid cooling, is provided